Subacute thyroiditis
Epidemiology
Etiology
Subacute granulomatous thyroiditis (De Quervain thyroiditis)
Subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis (≈ Postpartum thyroiditis)
Subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis is characterized by damage to follicular cells with lymphocytic infiltration resembling Hashimoto thyroiditis, rather than granuloma formation.
- Drugs: α-interferon, lithium, amiodarone, interleukin-2, tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- Autoimmune disease
- Postpartum thyroiditis
- Affects approx. 5% of women
- Most prevalent in women with:
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus
- History of postpartum thyroiditis
- Increased titers of thyroid peroxidase antibodies
- Occurs within 1–12 months of delivery
- Manifests with a period of transient thyrotoxicosis followed by hypothyroidism without thyroid enlargement or tenderness
- Associated with increased titers of thyroid peroxidase antibodies.
- Usually resolves spontaneously.
Pathophysiology
Subacute thyroiditis typically follows an acute viral illness and is thought to be due to a cross-reacting immune response against viral proteins or tissue antigens released during cellular injury.
- Thyrotoxic phase
- Lasts 2–8 weeks
- Caused by damage to follicular cells and the release of pre-formed colloid (stored thyroid hormones)
- Hypothyroid phase
- Typically lasts 2–8 weeks; permanent in ∼ 15% of individuals with subacute granulomatous thyroiditis
- Caused by depletion of pre-formed colloid and impaired synthesis of new thyroid hormones as a result of damage to follicular cells
- Euthyroid phase: Thyroid function recovers and pathological changes are no longer visible in the thyroid gland.
Tip
The disease is self-limiting in most cases but a few patients may experience relapses, and permanent hypothyroidism occurs in ∼ 15% of cases!
Clinical features
Subacute granulomatous thyroiditis (De Quervain thyroiditis)
- Possible history of upper respiratory tract infections a few weeks prior to the onset of subacute thyroiditis
- Very painful, diffuse, firm goiter, jaw pain
- Fever and/or malaise may be present.
- Features of hyperthyroidism followed by features of hypothyroidism
Mnemonic
- De Quervain causes pain.
- Associate the pain, fever with viral infection.
Subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis
- Painless, diffuse, firm goiter (thyroid size may be normal)
- The terms “silent” or “painless” thyroiditis are often used to describe subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis.
- Features of hyperthyroidism followed by features of hypothyroidism
Diagnostics
- Thyroid function tests
- Thyrotoxic phase: ↑ T3 and T4 , ↑ thyroglobulin, ↓ TSH
- The T4/T3 ratio is higher than in Grave's disease.
- Hypothyroid phase: ↓ T3 and T4, ↑ TSH
- Thyrotoxic phase: ↑ T3 and T4 , ↑ thyroglobulin, ↓ TSH
- Confirmatory test
- ↑ ESR
- Radioiodine uptake study : ↓ iodine uptake
- Iodine uptake decreases for two reasons: 1. Follicular cells are damaged and unable to take up iodine; 2. TSH secretion is initially suppressed as a result of thyrotoxicosis. Radioiodine uptake returns to normal when TSH begins to rise during the hypothyroid phase. Decreased iodine uptake is another important feature that differentiates Graves thyrotoxicosis from thyrotoxicosis that occurs with subacute thyroiditis.
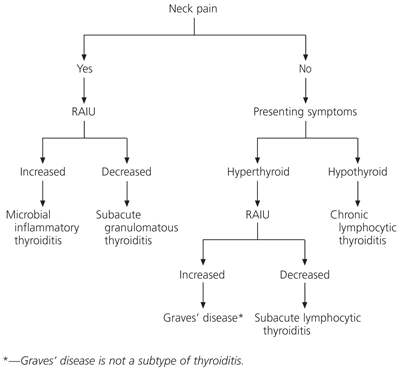
- Thyroid pain differential
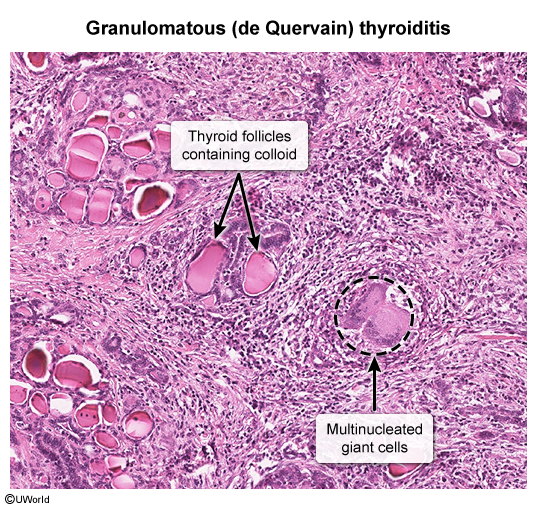
- Histology
- Subacute granulomatous thyroiditis: granulomatous inflammation, multinucleated giant cells
- Subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis: lymphocytic infiltration, sparse germinal centers
- Subacute granulomatous thyroiditis: granulomatous inflammation, multinucleated giant cells
Differential diagnostics
| Feature | Postpartum Thyroiditis (Subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis) | Hashimoto's Thyroiditis |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Autoimmune, triggered by pregnancy | Autoimmune, unrelated to pregnancy |
| Population Affected | Women postpartum | Any age, both genders, more common in women |
| Timeline | Within 1 year after childbirth or miscarriage | Chronic and progressive |
| Phases | Hyperthyroid → Hypothyroid → Recovery | Typically hypothyroidism developing over time |
| Risk Factors | Postpartum, type 1 diabetes, family history | Family history, other autoimmune diseases |
| Symptoms | Mild hyperthyroidism, then hypothyroidism | Symptoms of hypothyroidism, sometimes painless goiter |
| Potential Outcomes | Usually temporary, but some permanent cases | Often leads to permanent hypothyroidism |
| Treatment | Often none, temporary thyroid hormone therapy if needed | Lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy |